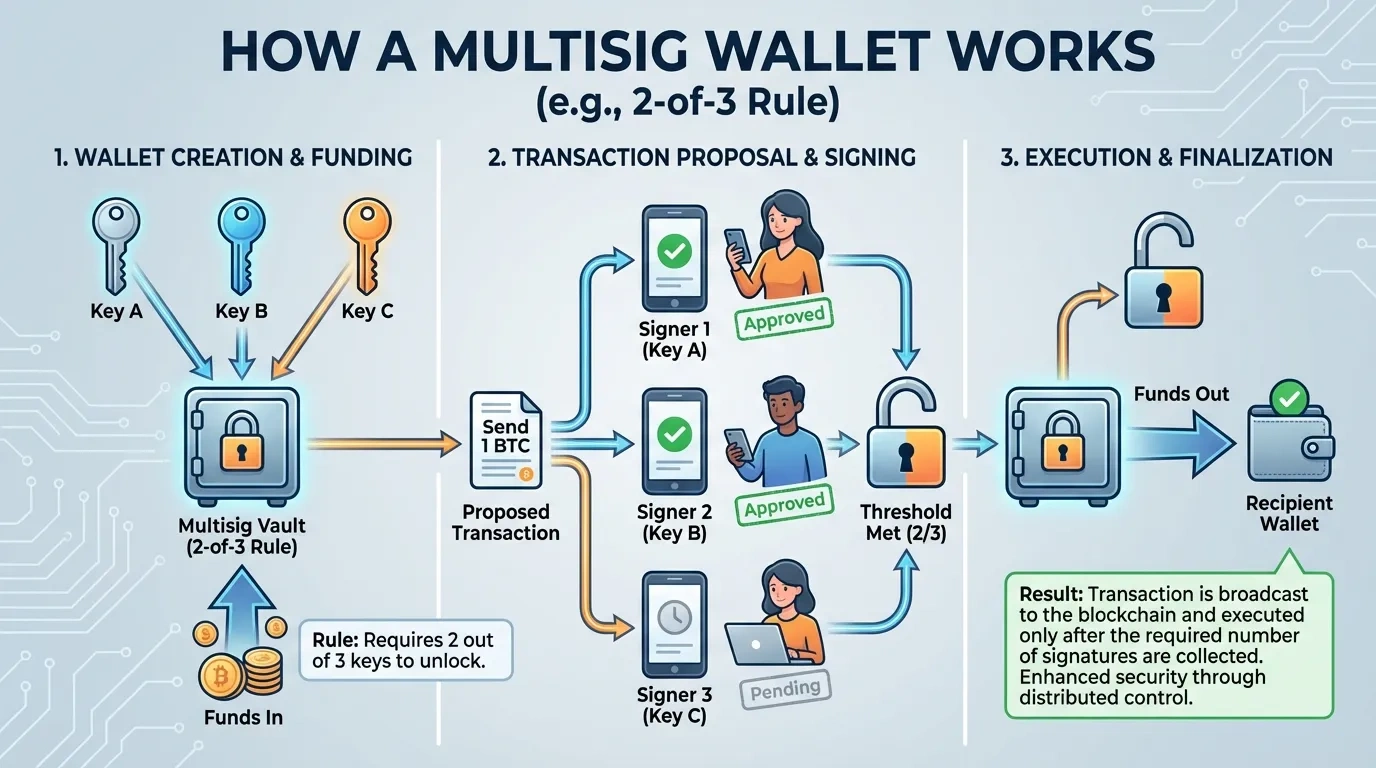
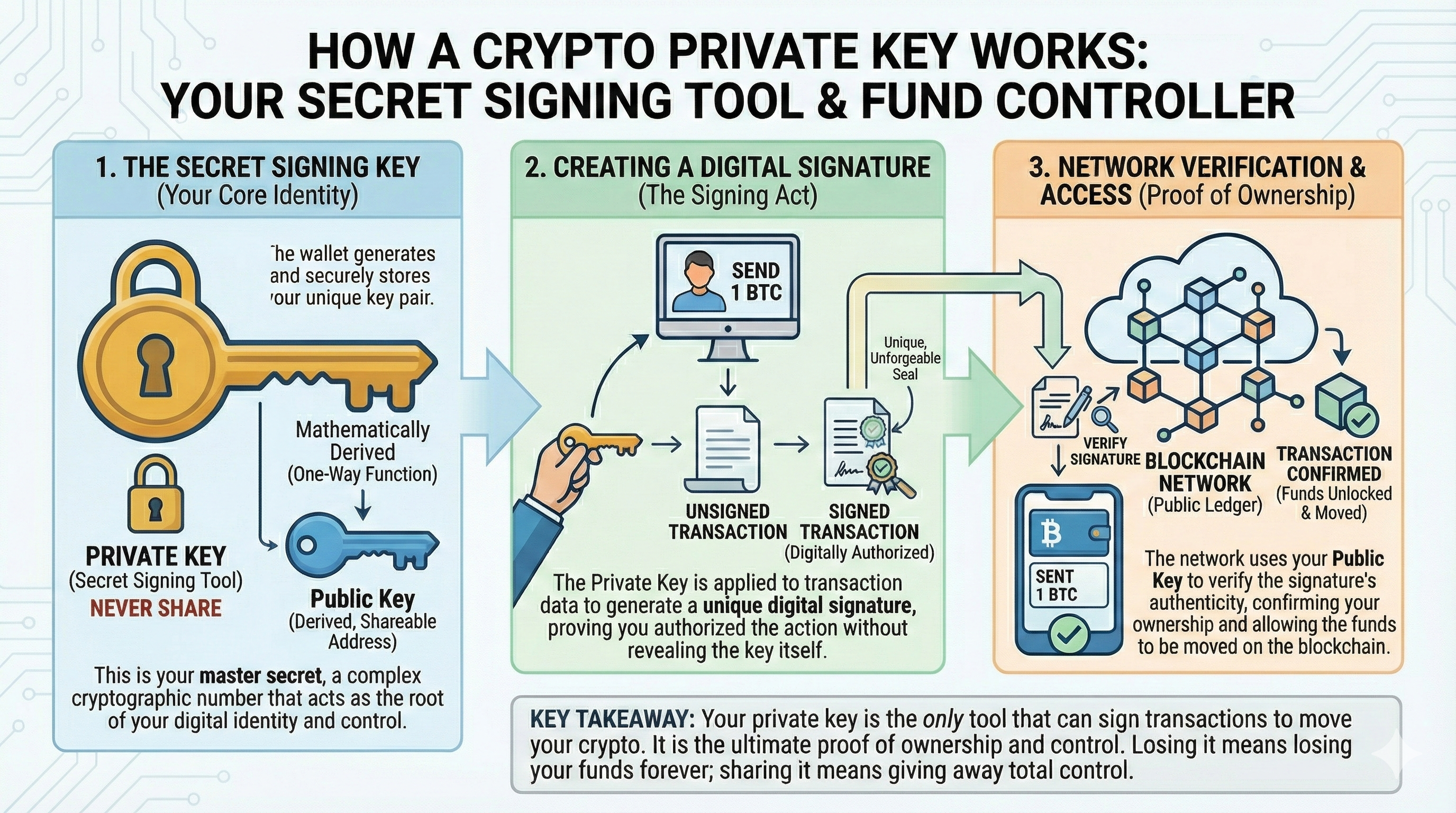
A public key is a cryptographically computed alphanumeric string that allows you to receive transactions, but it’s also used to verify your blockchain identity when sending. The public key is closely related to your wallet address, which is a shorthand version of the corresponding public key.
A public key is part of a public/ private key pair.
Your public key (or the wallet address derived from it) acts as a mailbox on the network. Anyone can use this public address to send you mail (assets). However, only you can access the contents because you have the private key.
This structure isn’t unique to cryptocurrency, but in a blockchain context, a public key is a way for the network to identify who the funds belong to without revealing your real-world identity or the private key that secures the funds.
The Bridge to the Ledger #
Notably, a Public Key and a Wallet Address are related but distinct.
- Your public key is the raw mathematical result derived from your private key, acting as the bridge between your secret data and the public ledger.
- An address is a simplified, hashed version of your public key, much like a fingerprint acts as an identifier for a person. Your wallet address acts as a pseudonymous identity on the blockchain.
For example, a Bitcoin public key is 130 characters long, compared to a Bitcoin wallet address, which ranges from 26 to 62 characters, depending on the format.
The Logic of Transparency #
Blockchains are built on “Public-Key Cryptography .” This allows for a system where every participant can verify that a transaction is valid without anyone needing to see the owner’s private key.
- Mathematical Derivation: A public key is generated from a private key using a process known as Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). This “one-way” street means you can easily turn a private key into a public one, but it’s computationally impossible to reverse the process.
- Public Verification: When you send a transaction, the network treats your public key as your identity and uses it to verify that your digital signature is valid. This allows the network to stay secure while remaining completely transparent.
- The Address Bridge: To improve readability and reduce errors, public keys are processed through hashing algorithms to create the addresses you see in your wallet. This creates wallet addresses of uniform length (depending on wallet type) that act as a digital fingerprint of the public key.
Why It Matters: Privacy & Models #
Understanding public keys is essential for safely navigating the world of self-custody, particularly regarding how different blockchains handle your privacy.
- Safety in Visibility: You can share your public key or address freely. Unlike your seed phrase , exposing your public key does not put your funds at risk of theft. It only allows others to send you money or view your transaction history.
- The UTXO Model (Bitcoin): Bitcoin treats addresses like unique invoices. Standard practice is to use a new public address for every transaction. This “Address Rotation” makes it much harder for outside observers to link multiple transactions to a single person’s total net worth.
- The Account Model (Ethereum): Ethereum works like a traditional bank account. You have one persistent public address, and all your ETH, tokens , and NFTs are tied to it. This makes tracking and interacting with smart contracts easier, but it means your entire balance and history are visible to anyone who knows that one address.
The Debrief #
A public key is the transparent face of your digital independence. This pseudonym string of letters and numbers allows the world to interact with your wallet while keeping your private keys safely hidden behind one-way mathematical walls. However, any link between your real and pseudonymous identities provides a breadcrumb trail that can expose your blockchain activity.